 |
| Hip adductor strain groin pain in soccer (Ref: https://www.limpinleapoutphysiotherapy.com.au/blog1/groin-pain-in-soccer-players) |
There are several musculoskeletal disorders involve groin pain, for example, osteitis pubis, Insertional adductor and rectus abdominis tendinopathy, Apophyseal avulsion fractures, Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) syndrome that hip adductors strain is one of the most common injuries in athletes.
Normally, groin injuries make up 2% – 5% of all sport ‑ induced injuries, of which adductor strain is the usual musculoskeletal etiology of the pain. The most common sports that put athletes at risk for adductor strains are football, soccer, hockey, basketball, tennis, figure skating, baseball, horseback riding, karate, softball, and cricket.
Hip adductors strain have risk multifactorial; include, different forms of sports, high level of play, age and core stability, previous hip adductor injury, hip adductor - to - abductor strength imbalance, and adductor tightness.
 |
| Anterior thigh view with hip adductor are in medial side (Ref: https://www.britannica.com/science/quadriceps-femoris-muscle) |
Hip adductor muscles shortening affected pelvic tilt posture both of anterior - posterior plane and lateral plane. The position is one of lateral pelvic tilt, with the pelvis so high on the side of contracture in standing. Legs alignment would be changed because of this deformity. Tightness of secondary hip flexors, such as adductor brevis, gracilis, and anterior fibers of the gluteus minimus, would, in theory, contribute to an excessive anterior pelvic tilt and exaggerated lumbar lordosis.
Some hip adductor fibers which arise from the anterior surface of pubic will assist to flex the hip joint. By the way, all of them contract to adduct and internally rotate the hip joint.
7 ways to stretch hip adductors
Exercise #1: stand hip abduction with lateral pelvic shift stretch: spread both legs 2 - 3 times shoulder wide. Then, tilt up the opposite pelvic side of target leg laterally.
Exercise #2: stand lateral lunge stretch: spread both legs 2 - 3 times shoulder wide. Then, bend supported leg like lateral lunge squat to stretch target leg which is opposite side.
Exercise #3: supine frog stretch: For standard stretching, keep both feet together during stretching. For advance stretching, separate both feet away.
Exercise #4: modified lion stretch: keep both feet together during stretching. Control hips in extension postition, not back extension.
Exercise #5: figure of 4 stretch: for more stretch, we needs move knee close to floor as far as possible.
Exercise #6: Half kneeling lateral shift stretch: it is used for stretching leg which is kneeling.
Exercise #7: stand lateral lunge with hip extension stretch: spread both legs 2 - 3 times shoulder wide with hands are on the wall. Then, target leg turn to toe out. And supported leg step forward to prepare squating. Supported leg squat with shift weight forwatd and laterally for position target leg in hip extension, hip external rotation, hip abduction.
A common mechanism of the injury is sudden change of direction or violent external rotation with abduction at hip joint while the foot is planted on ground with eccentric contraction that my patients and I underwent before. The most common hip adductor strain is hip adductor longus.
Once, I got a hip adductor strain during soccer games. It happened very fast, I stepped my right leg to the ball with poor leg position because of fatigue. Then, I stepped my left leg to the right to keep balance and play on. Suddenly, my torso twisted with a "pop sound" at my left hip. I fell on the ground and was carried afterward. I had stopped all my exercise for 4 months.
The five primary hip adductors include the pectineus, gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, and adductor magnus (both anterior and posterior heads). Secondary adductors include the biceps femoris (long head), the gluteus maximus (especially the posterior fibers), quadratus femoris, and obturator externus.
The muscles testing and function textbook which was written by Kendall, stated primary hip adductors anatomy that:
The pectineus arise at the surface of superior ramus of the pubis ventral to pecten between ilioppectineal eminence and pubic tubercle, and inserted at pectineal line of femur distally.
 |
| Pectineus muscle (Ref: https://michael-loehr.com/muscles-of-the-lower-limb/) |
The adductor magnus derived tendon at inferior pubic rami, ramus of ischium (anterior fiber), and ischial tuberosity (posterior fibers), then had insertion at medial to gluteal tuberosity, middle of linea aspera, medial supracondylar line, and adductor tubercle of medial condyle of femur.
 |
| Hip adductor magnus (Ref: https://michael-loehr.com/muscles-of-the-lower-limb/) |
The origin of adductor brevis was at the outer surface of inferior ramus of pubis, and had distal attachment at distal two thirds of pectineal line, and proximal half of medial lip of linea aspera.
 |
| Hip adductor brevis (Ref: https://michael-loehr.com/muscles-of-the-lower-limb/) |
The adductor longus had origin not far from its friends which is the anterior surface of pubis at junction of crest and symphysis, and had insertion at the middle one thirds of medial lip of linea aspera.
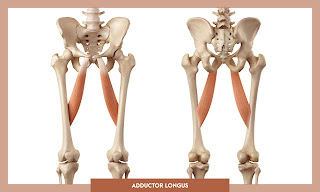 |
| Hip adductor longus (Ref: https://michael-loehr.com/muscles-of-the-lower-limb/) |
The gracilis started at the inferior half of symphysis pubis and medial margin of inferior ramus of pubic bone, then passed on medial side of femur to the medial surface of body of tibia, distal to condyle, proximal to insertion of semitendinosus, and lateral to insertion of sartorius. It is only one muscle which is two joint muscle of hip adductor group.
 |
| Gracilis (Ref: https://michael-loehr.com/muscles-of-the-lower-limb/) |
All of the above provide adduct hip joints, majorly. The pectineus, adductor brevis, and adductor longus flex the hip joint. The anterior fibers of the adductor magnus which arise from the rami of the pubis and ischium may assist in flexion, while the posterior fibers that arise from the ischial tuberosity may assist in extension. The gracilis, in addition to adducting the hip joint, flexes and medially rotates the knee joint. In addition to hip adduction, these muscles help stabilize the hip and lower limbs during the standing phase of the gait. Therefore, their function consists of hip adduction, hip flexion, hip internal rotation, and some fibers of them assist hip extension.
Reference:
https://www.jospt.org/doi/epdf/10.2519/jospt.2010.3025
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/270251533.pdf
https://aassjournal.com/article-1-1057-en.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4714133/pdf/10.1177_2325967115625055.pdf
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317366152_Assessment_and_management_of_adductor_strain




ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น