 |
| Roman chair exercise (Ref: https://barbend.com/) |
Flat-back syndrome is characterized by forward inclination of the trunk, inability to stand upright, and LBP that decreases the lumbar lordosis of the spine. The decreased lumbar spine lordosis induces changes in absorbing shock between vertebrae, and creating stresses in spinal muscles, tendons and ligaments. The ideal curvature of the spine in the sagittal plane serves to reduce loads on the vertebral discs and any shock to the spine, and it allows effective action of the spinal muscles.
The presence of a flat back is associated with malalignment in the spine, which could cause dysfunction of the deep lumbar muscles and result in chronic low back pain and deep muscle atrophy. Several studies have demonstrated atrophy of the lumbar multifidus muscles with infiltration of fatty tissue in patients with chronic LBP and atrophy at the dysfunctional lumbar level.
 |
| Lumbar erector spinae and multifidus muscles (Ref: https://centenoschultz.com/) |
The lumbar paraspinal muscles is the neighbor which can be progressively loaded during extension exercises by utilizing back exercise units that will tilt the pelvic to different degrees. As one progresses from a more upright position to a more horizontal position, the exercise becomes more intense for the back extensors. Once a patient can perform the exercise in the prone horizontal position. Sitting extension exercises performed with specialized equipment are also a good way to strengthen the low back musculature, because the resistance can be progressively increased. It has been demonstrated that the exercise activates the low back muscles better if the pelvis is mechanically stabilized so that the extension movement comes from the spine rather than from the hip extensors.
Some studies have shown that in individuals with LBP, moreover, there is also a decrease in the strength and lengthening of the iliopsoas, due to the connection of this muscle with the pelvis and the lumbar spine. As a result of this attachment, the iliopsoas possibly has a stabilizing role in the column. It is thought that tension in this muscle, formed by the union of the psoas major, psoas minor and the iliac acts bilaterally with the insertion, causing an increase in lordosis, whereas weakening of the muscle reduces its size where both these conditions result in pain.
 |
| Force direction of hip flexor (iliacus & psoas) and lumbar back extensor (Ref: https://www.sydneyphysioclinic.com.au/) |
All of these above muscles are members of pelvic and lumbar stabilizer or core stability muscles. Physiotherapists utilize exercise therapy as an intervention for patients with LBP. The spinal stabilization exercise approach has become popular with many therapists. Physical therapists tend to take different approaches when rehabilitating the muscles of the low back in patients.
Due to the lumbar multifidus and erector spinae muscles have a relatively high proportion of type I (slow-twitch) muscle fibers. These muscles have fiber composition that makes them well suited for endurance or sustained contraction activities.
 |
| Floor exercise for low back is low impact exercise (Ref: https://www.popsugar.com/) |
There is no evidence in the literature that one exercise program is superior to another. Using low-load stabilization exercise makes them well suited for endurance or sustained contraction activities. So, this topic maintained variation of basic lumbar exercise to treat LBP from flat back posture.
The second basic 10 of 20 therapeutic strengthening exercises to activate anterior tilt (Remark: If there is tightness of the abdominal muscle or hamstring, it is necessary to treat these muscles to restore normal length before the abdominals can be expected to function optimally.)
Each exercise needs 10 - 15 reps with 3 sets for 3 - 5 days a week.
Exercise #1: Supine hip external rotation with band: exercise with loop band or make band to be loop which need slight heavy resistance. Separate both knees to the floor with slight slow speed both downward and upward directions.
Exercise #2: Heel slide to hip flexion
Exercise #3: Supine hip flexion: In case of too short legs, I would like to recommend you to put some things under your foot at starting position.
Exercise #4: Upper back extension: If you exercise on the bench that will be call Roman chair exercise.
Exercise #6: Chair pose: During bending the knees, you have to maintain the space between both knees.
Exercise #7: Stand pelvic anterior tilt: Start with bend both knees slightly. Then arch your lumbar spine.
Exercise #8: Lunge: During lunge, do not let knee be inward direction that is keeping knee point to in front. Start with forward - backward stance and move body downward and upward vertically.
Exercise #9: Deadlift: The movement consists of bend knees slightly and straight lumbar with bend over.
Exercise #10: Unidedal deadlift: It combines of straight lumbar bend over with elevate leg to hip level and opposite hand touch the floor.
The system of local stabilization involves deep intrinsic muscles which are directly attached to the lumbar vertebrae, and the global system comprises the great superficial muscles originating in the pelvis which insert in the thoracic cavity, with both systems necessary for stability and control of movements.
The erector spinae and multifidus muscles are the primary muscle groups responsible for controlling lumbar motion and forward inclination of the trunk. It is estimated that the erector spinae and multifidus contribute up to 85–95% of extensor moment during manual handling tasks, with these muscles playing an important role in resisting anterior shear forces during lifting and lowering.
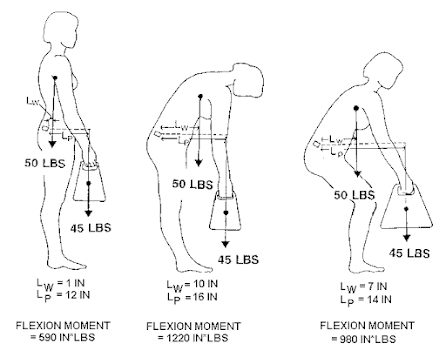 |
| Load on lumbar spine in different lifting posture (Ref: https://ouhsc.edu/) |
The erector spinae and multifidus muscles are thought to play an important role in the prevention of back injuries, and these muscles are often targeted during the rehabilitation of patients with such injuries. For example, during vocational activities such as lifting, the erector spinae and multifidus muscles are the major contributors to the extensor moment and serve to resist anterior shear forces acting on the lumbar spine.
Core stabilization exercises aim to maintain this stability, improve strength, resistance, improving neuromuscular control of the abdominal and lumbar muscles, and attenuating recurrent LBP. Stabilization exercises are essential in order to provide a base for movement of the arms and legs when supporting weight and to protect the medulla and spinal nerves. Exercise stabilization programs emphasis on the transverse abdominis and multifidus (deep trunk muscles). Paravertebral and abdominal muscles such as the pelvic musculature and the diaphragm are also important targets for exercise.
 |
| Upright with torso bending contributes increased lumbar disc pressure and multifidus workload (Ref: https://ergonomictrends.com/) |
80% to 90% of patients with acute LBP seem to recover within 6 weeks, regardless of the treatment received. In spite of this, there is about a 60% recurrence rate of LBP in patients within 1 year of the initial episode. Some patients do not recover from the acute LBP episode and go on to have a chronic condition. LBP is one of the leading causes of incapacity and the high cost of treatment renders preventative strategies paramount. Therefore, proper LBP prevention and treatment can help you to maintain daily life living capacity and save money.
Reference
Kendall FP., et al. Muscles testing and function. Fourth edition. Williams & Wiikins. USA.
1993.
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/20/10923/htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5342962/
https://www.scielo.br/j/rbfis/a/HjjyDzqVhbvDxkCSHqnWkjs/?format=pdf&lang=en
https://www.scielo.br/j/fm/a/z6pw7PhWLtMQDGWyZCmYP7c/?lang=en&format=pdf
https://www.jospt.org/doi/pdf/10.2519/jospt.2008.2865





ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น